BLOG
POPULAR ARTICLES
Beyond the Bottle: Unexpected Applications of Recycled PET in Everyday Life
27 May, 2025

Commonly discarded plastic bottles have silently become crucial ingredients in many products used daily. Far from mere waste, these items now serve as valuable products thanks to advanced recycling techniques. Leading companies like Pashupati Group lead efforts to convert what was once trash into resources for everything from fashion to infrastructure.
The following article reveals how waste bottles transform into valuable new products, examining both current applications and future possibilities in sustainable manufacturing.
From Trash Bin to Factory Floor: How Plastic Bottle Recycling Transforms Waste
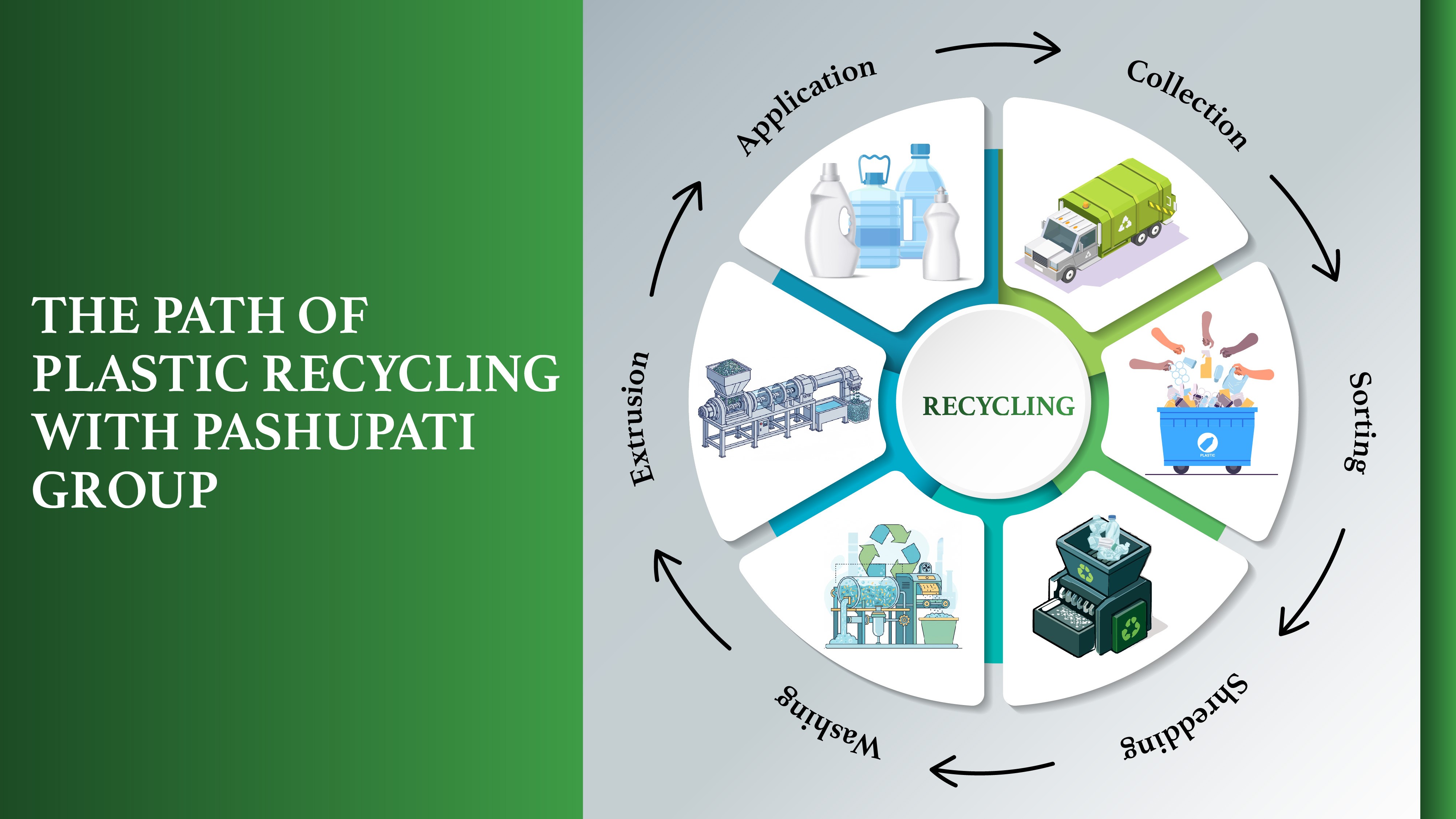
The PET Transformation Journey
Most drinks bottles never truly die; they simply change form. After collection, these PET (polyethylene terephthalate) containers pass through sophisticated plastic bottle recycling plant locations where sorting, washing and shredding occur. Pashupati Group operates such facilities with remarkable efficiency.
The process starts with waste inspection, various types of sourcing through machine and labour, removing labels, grinding to create small particles, hot chemical washing, drying, and sorting to get PET flakes. These flakes are then converted to rPSF or r-PET chips through a separate process, becoming the foundation for countless new goods. What began as temporary packaging thus gains permanent purpose through technical innovation.
This approach delivers dual benefits: economic savings paired with ecological advantages. Recycled material requires approximately 70% less energy than virgin polyester manufacturing whilst dramatically reducing water usage. Perhaps most significantly, effective recycling addresses plastic pollution, a critical environmental threat affecting ecosystems worldwide.
Unexpected Applications of Recycled PET
rPSF manufacturers have developed diverse applications for recycled PET beyond creating new bottles. Several examples illustrate potential future uses for discarded bottles:
Textile and Footwear Industries
Recycled PET constitutes an increasing proportion of polyester clothing. Approximately 12 bottles suffice to produce one T-shirt. Sportswear, outerwear, luggage, and footwear brands increasingly incorporate rPSF or r-PFY.
Multiple international companies have pledged exclusive use of recycled polyester in forthcoming products. Indian manufacturers follow suit, driven by increasing consumer demand for ethical fashion options.
Automotive Uses
Car makers integrate recycled PET bottles into numerous interior components. Seat fabrics, instrument panel insulation, acoustic barriers and carpet backing car headliner all contain materials derived from plastic waste.
Adopting these alternatives lets auto companies reach green targets without compromising build quality. Environmental certification programs recognise these efforts, awarding credentials that boost corporate standing. Despite limited consumer awareness, automotive applications now consume substantial quantities of recycled plastic annually, creating significant market demand.
Household Products
Recycled PET transforms into countless home items. Bedding manufacturers fill pillows, duvets, and mattress padding with fibres derived from plastic bottles. Similarly, carpet producers incorporate these materials into flooring solutions. The molecular structure of processed PET creates products that resist moisture damage and maintain shape over extended periods.
Hotels, restaurants, and residential buildings increasingly select rPET products due to environmental benefits combined with practical advantages. The hypoallergenic nature of properly processed recycled polymers makes these materials particularly suitable for allergy-prone individuals.
Food Packaging
When properly processed, rPET proves safe for food packaging applications, increasingly evident in supermarkets and delivery services.
Brands utilising rPET packaging reduce carbon emissions and gain regulatory advantages under India's Plastic Waste Management Rules.
Industrial Packaging Solutions
Industries requiring robust packaging utilise rPET-based strapping and fibres to secure goods during transportation and handling.
These bindings offer strength, recyclability, and growing popularity as alternatives to traditional metal or virgin plastic equivalents.
Advanced Production Techniques
Several 3D printing material suppliers now offer filaments made from processed bottle waste. These products serve designers who prioritise sustainable material sources without sacrificing print quality.
The growth of digital fabrication across manufacturing sectors creates new outlets for recycled plastics. Projects ranging from architectural models to custom product parts increasingly utilise these eco-friendly materials, cutting waste while delivering required performance.
Pashupati Group: Industry Leader
Pashupati Group stands among leading rPSF manufacturers in India, operating sophisticated facilities that convert discarded bottles into industrial-grade fibers. Their production systems balance maximum output with minimal environmental impact through advanced plastic recycling processes.
Annual processing capacity reaches many thousands of tons, setting industry standards for large-scale operations. Customers span diverse sectors including textile production, vehicle manufacturing, construction systems, and consumer packaging.
Quality control remains central to company operations. Rigorous testing ensures materials meet global standards while maintaining complete supply chain documentation. Manufacturing partners value this reliability when implementing sustainability initiatives that require consistent performance.
Why Recycled Polyester Staple Fiber Matters
Four key factors drive rPSF adoption across multiple industries:
- • Raw Material Reduction: Decreases need for petroleum-based virgin polyester
- • Resource Efficiency: Cuts energy consumption and water usage during production
- • Cross-Industry Application: Serves markets from clothing to industrial packaging
- • Cost Effectiveness: Offers competitive pricing compared to traditional alternatives
These properties allow companies to maintain existing product performance while addressing environmental concerns. The material creates practical paths toward manufacturing systems that balance ecological and economic priorities.
Future Innovations
Market dynamics increasingly favour recycled materials as sustainability becomes essential rather than optional. Several developments appear on the horizon:
Technological Advancements
Improvements in automated sorting systems will reduce contamination, enhance output quality, and increase plastic recycling process efficiency.
AI-based systems and robotics undergo testing in European and North American facilities, with Indian recyclers exploring similar upgrades to maintain competitiveness.
Enhanced Product Engineering
Manufacturers increasingly design products considering end-lifecycle recyclability, facilitating more straightforward and economical future recycling.
This includes mono-material utilisation, avoiding toxic colourants, and clear packaging material labelling, all supporting more efficient recycling processes.
Regulatory Frameworks
India and other nations enforce stricter Extended Producer Responsibility regulations. Companies like Pashupati Group are strategically positioned to assist brands in meeting these requirements.
As compliance transitions from optional to mandatory, recyclers with robust infrastructure will assume greater significance in helping brands achieve targets.
Market-Driven Changes
With growing awareness, consumers increasingly select products manufactured from recycled content. Transparent sourcing and traceability become competitive advantages.
Eco-labelling, carbon metrics, and QR-code traceability assist environmentally conscious consumers in making informed decisions, particularly regarding fashion and packaging.
Material Innovation
Beyond PET, other recycled plastic forms may gain prominence, including biodegradable composites and ocean-sourced plastics.
Pashupati Group and similar organisations currently invest in research exploring future-oriented solutions extending beyond conventional recycling methodologies.
Conclusion
While water bottle recycling appears straightforward, its impact extends throughout daily life. From clothing to construction materials, recycled PET transforms waste into valuable resources. Pashupati Group continues developing systems supporting this transition towards circular manufacturing principles.
A discarded bottle potentially becomes raw material for clothing, vehicle components, or building insulation. This transformation from waste to resource proceeds steadily, with Pashupati Group amongst the pioneering organisations. Sustainability emerges gradually through systematic processes, converting bottles to fibres and ultimately into essential everyday products.
RECENT BLOGS